Bleeding and bruising disorders
Apr 19, 2022
Bleeding disorders are a group of conditions when blood cannot clot properly. Normal clotting involves platelets, proteins in the blood called clotting factors. Bleeding and bruising can occur from either too few or abnormal platelets, abnormal or low amount of clotting factors or abnormal blood vessels.
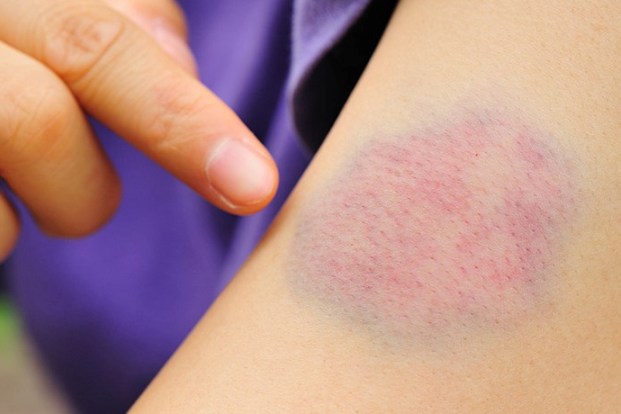
Causes of abnormal bruising:
- Thrombocytopenia (low platelets) –
Can be caused by infections, drugs, malignancy, bone marrow infiltrative diseases, vitamin B12 deficiency, collagen vascular disorders, chronic liver disease, immune thrombocytopenic purpura.
- Platelet function disorders
- Senile purpura
Causes of abnormal bleeding:
- Hemophilia is the most well-known inherited bleeding disorder.it affects predominantly males.Hemophilia is a rare, inherited bleeding disorder that can range from mild to severe. Severity depends on the deficiency of clotting factors. Hemophilia is classified as type A or type B. in type A factor VIII is deficient, in type B factor IX is deficient. Hemophilia results from a genetic defect found on X chromosome.
- Other inherited bleeding disorder is von Willebrand disease. It can affect both males and females.
- Vitamin K deficiency
- Platelet disorders are the most common cause of bleeding disorder and are usually acquired.
Symptoms of bleeding disorders may include:
- Easy bruising – Development of bluish patches over the skin, mainly forearms, thighs and back
- Bleeding gums – Spontaneous bleeding or bleeding due to trivial trauma or injury
- Excessive bleeding from small cuts – Trivial injury can cause excessive bleeding even from the smallest cuts
- Excessive bleeding from dental procedure – Minor dental procedures can cause bleeding
- Epistaxis which is unexplained – Bleeding from nose where there is no obvious local cause
- Bleeding in the joints – Spontaneous bleeding or bleeding after trivial trauma can occur in the knee joints
Investigations that can be done to know the cause may include :
Complete blood count – To see platelet count
Prothrombin time (PT) – For diagnosis
Activated partial thromboplastin time(aPTT) – For diagnosis
Peripheral blood smear – To look for any abnormal cells
Liver function test – To evaluate for chronic liver disease
Renal function test – To evaluate for chronic kidney disease
Platelet function activity – To see for factor inhibitors
Mixing studies and inhibitor and Factor assays – To evaluate for connective tissue disorders and diagnose hemophilia or von Willebrand disease
Treatment should be according to the cause.









