Piles : Causes Symptoms & Surgery
Apr 19, 2022
Hemorrhoids are a very common anorectal (relating to the anus and the rectum) condition defined as the symptomatic enlargement and distal displacement of the normal anal cushions. They affect millions of people of all age groups around the world and represent a major and socioeconomic problem.
The word Hemorrhoid is derived from the Greek words,haem (blood) and rhoos (flowing),meaning flowing of blood.The word piles is derived from the latin word pila which means pill or a ball. The exact prevalence is difficult to estimate as patients hide it and do not come for consultation.
Types of Piles:
Classification 1
- Internal Piles:– Above the dentate line.
- External Piles:- Both occurs together.
Classification 2
- Primary Haemorrhoids :-located at 3,7,& 11 o’clock Related to the branches of the superior haemorrhoidal vessel,which divides on the right side in two and on left side continues as one.
- Seconadary Haemorrhoids:- One which occurs between the primary sites.
- Classification 3
- Degree Piles:- May bleed but does not come out .
- Degree Piles:- Prolapse during defecation,but returns back spontaneously.
- Degree piles:- prolapsed during defecation,but replace back manually.
- Degree Piles:- Permanently prolapsed.
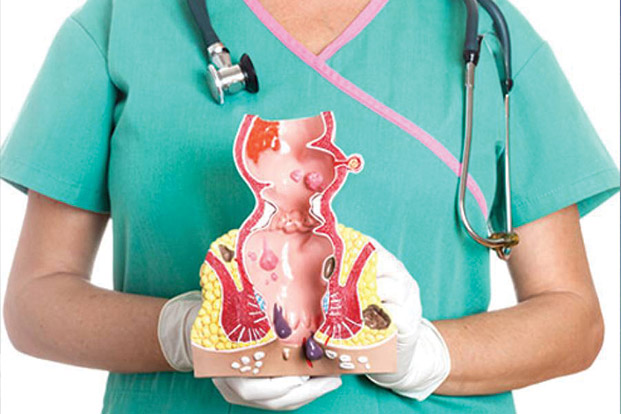
Causes of Piles :
- It is downward sliding of anal cushions abnormally due to straining.
- The rich plexus of vascular under the anal canal and lower rectal mucosa is called corpus cavernosum recti which connects arteries and veins without intervening capillaries.It was associated with bright red bleeding. Anal cushions are aggregation of blood vessels (arterioles,venules),smooth muscles and elastic connective tissues in the submucosa that normally reside in the left lateral,right posterolateral and right anterolateral and canal.
- The vascular cushions have physiological role in maintaining anal continence .These cushions provide complete closure of the anus due to engorgement following coughing,sneezing,etc.When there is raised intrarectal pressure.
- Piles can be mucosal or vascular. Vascular type is seen in young, mucosal is seen in old patients.
- Erect posture of humans leading to increased stasis/pressure at the lower end is a contributing factor to develop piles.
- Absence of valves in the hemorrhoidal sinusoids,Obstruction to venous return,and weakening of park’s ligaments (Trietz muscle).Repeated stretching of anal canal mucosa causes weakness of the supporting tissue thereby causing haemorrhoids.
- In Pregnancy, increased vascularity and laxity of pelvic floor muscles along with abdominal compression of major veins predispose to higher incidence of hemorrhoidal disease especially in late pregnancy.
- Hard Stool,low fiber diet,over purgation.
- Carcinoma of rectum.
- Portal Hypertension.
Clinical Features Signs & Symptoms of Piles:
- Mostly seen in 30 to 65 age group.
- Equal incidence in both sexes.
- Bleeding-Splash in the pan-bright red & fresh blood.
- Mass per anum.
- Pain-Normally painless,but pain indicates some complications.
- Anemia.
- Pruritus.
Clinical Examination done for Diagnosing Piles:
- On inspection-Prolapse piles seen.
- Per Rectal Examination- only thrombosed piles felt.
- Through Proctoscopy-exact position made out.
- Ideally proctosigmoidoscopy should be done.
Treatment for Piles:
- Non Operative treatment options for piles are:
- Avoid constipation & undue straining.
- Opt for a Fiber diet.
- Use a Laxative.
- Opt for a Sitz bath.
- Use Anti inflammatory drugs.
- Local application (to reduce pain,oedema).
Parasurgical treatment options for Piles:
- Injection sclerosant therapy.
- Rubber band ligation (Barron’s branding).
- Infra red coagulation.
- Laser therapy-Nd- Yag,diode & carbondioxide lasers.
- Doppler Guided Haemorrhoidal artery ligation (DGHAL).
Surgical option for treatment of Piles:
- Open method-(Milligan-Morgan).
- Closed method –(Hill Ferguson
- Stapled Haemorrhoidectomy: It is minimally invasive technique,circumferential excision of the mucosa and sub-mucosa 4 cm above the dentate line.


