Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension(PAH)
Apr 19, 2022
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension(PAH)
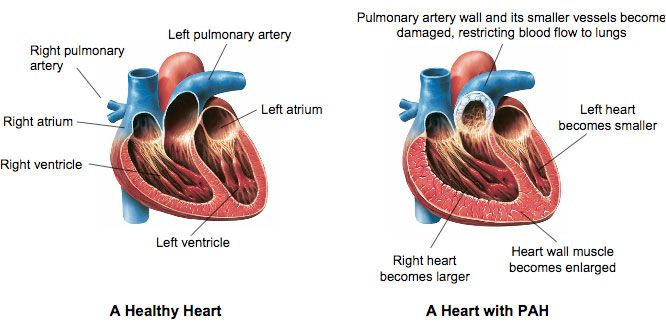
- Pulmonary hypertension is abnormally high blood pressure in the Pulmonary arteries.
- Pulmonary hypertension (PH) defined as a mean pulmonary arterial (PA) pressure of greater than 25 mm Hg at rest or greater than 30 mm Hg during exercise, is characterized by a progressive and sustained increase in pulmonary vascular resistance that eventually leads to right ventricular (RV) failure.
- Normal blood pressure in Pulmonary arteries ranges from 8 – 20 mm Hg at rest.
Classification:
In the conventional classification, pulmonary hypertension is divided into two main categories:
1) Primary (Idiopathic) Pulmonary Hypertension (not caused by any other disease or condition)
2) Secondary Pulmonary Hypertension (caused by another underlying condition). Secondary pulmonary hypertension is more common than primary pulmonary hypertension.
Symptoms
- B– Bluish Lips, hands, and feet
- L– Lightheadedness
- U– Uneasy to breath
- E– Edema
- S– Syncope
Precautions to be taken:
Self-Management Options
Effective self-management is important. By taking the following steps patient can improve their overall quality of life and slow the progression of symptoms. Lifestyle modifications can help to improve the PAH condition.
- Eat food rich in nutrients like potassium, magnesium, and vitamins
- Reduce sodium intake
- Eat high fiber food (whole grains, beans, fruits, and vegetables)
- Maintain a healthy body weight
- Quit smoking and alcohol
- Stay active as much as possible
To prevent complications
- Avoid traveling/visiting high altitudes
- Before planning for pregnancy need to discuss with their doctor.
- Avoid climbing stairs & Weightlifting.
- If you find any above symptoms immediately visit your health professionals (Doctors) because early diagnosis of PAH is very important, this will help to maintain a good quality of life.









