Brain Haemorrhage
Apr 19, 2022
Brain haemorrhage is a loose term encompassing a variety of conditions where there is bleeding inside the cranial cavity. The bleeding may occur as a result of injury or may occur spontaneously. Spontaneously occurring brain haemorrhages are:
1. Sub arachnoid haemorrhage
2. Intracerebral haemorrhage
3. Subdural hematoma.
Sub arachnoid haemorrhage (SAH)- SAH occurs most commonly occurs due to head injury.
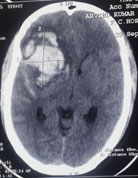
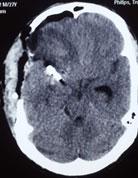
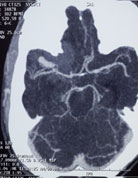
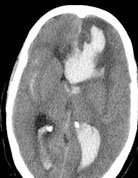
Second most common and serious cause of SAH is intracranial aneurysm. An aneurysm is a balloon like outpouching from blood vessels supplying the brain. Aneurysms may arise due to various reasons like high blood pressure, collagen vascular disease, smoking, polycystic kidney disease etc. These remain undetected till they rupture and bleed. Symptoms are sudden severe headache with vomiting and loss of consciousness. The patient may or may not regain consciousness depending on the degree of injury caused to the brain. Patients who survive may have rebleeding within next forty-eight hours and may die. Therefore, such patients should immediately be taken to a hospital to confirm SAH where it is diagnosed by doing a CT scan of brain. If SAH is confirmed then the next step is to do a DSA or CT angiography of the brain to detect the aneurysm, its location and anatomy.
Once it is confirmed that the patient is having an aneurysm that has ruptured and caused brain haemorrhage then it must be treated by surgery (clipping) or coiling (by endovascular means) to prevent further rupture and haemorrhage
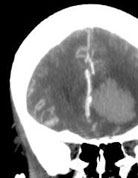
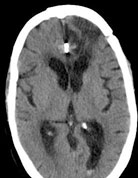
Below is the scan of a young male patient with bleed from an aneurysm. Before surgery patient was unconscious with paralysis of left side of body. After surgery the patient became conscious and his paralysis improved completely.