What to do when you have Stroke?
Apr 19, 2022
What is Stroke?
Stroke is also called as Brain Attack. It is a paralysis attack in which person loses power of any body part. It is caused by blockage in the arteries supplying blood to the brain. In some cases it is caused by rupture of artery inside the brain because of which a blood flows in brain substance and a clot gets formed.
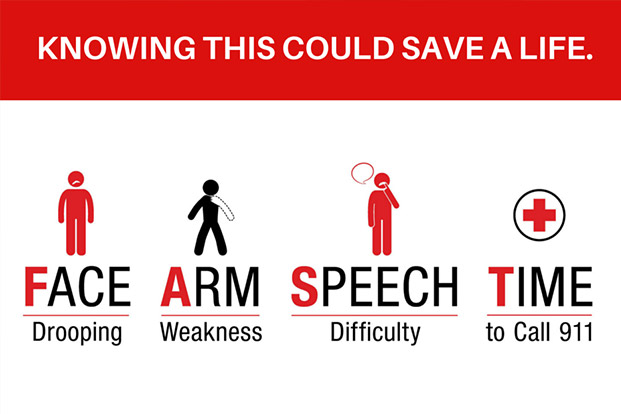
What are symptoms of brain attack/ Stroke?
You can feel following symptoms.
- Sudden inability to lift arm, grip objects from hand.
- Difficulty in walking, or imbalance while walking.
- Slurring of speech, asymmetry of face.
- Inability to talk or understand correctly
- Sudden headache
- Drowsiness or unconsciousness
- Sudden dizziness, problem in seeing , difficulty in swallowing.
These symptoms appear over minutes to hours , can appear in sleep. Such problems commonly appear during sleep and person may confuse these symptoms to be due compression hand or leg during sleep.
Are there varieties of Stroke?
The two forms of stroke are ischemic — blockage of a blood vessel supplying the brain, and hemorrhagic — bleeding into or around the brain. In an ischemic stroke, a blood clot blocks or plugs a blood vessel or artery in the brain. About 80% of all strokes are ischemic. In a hemorrhagic stroke, a blood vessel in the brain breaks and bleeds into the brain. About 20% of strokes are hemorrhagic.
What happens in stroke?
When a stroke occurs the blood supply to part of the brain is suddenly interrupted. Brain cells die when they no longer receive oxygen and nutrients from the blood or there is sudden bleeding into or around the brain.
What should one do during stroke ?
During a stroke, bystanders should know the signs and act in time. If you believe someone is having a stroke – if they lose the ability to speak, move an arm or leg on one side, or experience facial paralysis on one side – call neurologist immediately. Stroke is a medical emergency. Immediate treatment may save someone’s life and enhance his or her chances for successful rehabilitation and recovery.
What is the treatment for stroke?
Ischemic strokes, the most common strokes, can be treated with a drug called TPA which dissolves artery-obstructing clots. The window of opportunity to use TPA to treat stroke patients is three hours, but to be evaluated and receive treatment, patients need to get to the hospital within 60 minutes.
What are the risk factors for stroke?
There are things you can do to lower your risk of stroke. High blood pressure increases your risk of stroke four to six times. Heart disease, especially a condition known as atrial fibrillation or AF, can double your risk of stroke. Your risk also increases if you smoke, have diabetes, sickle cell disease, high cholesterol, or a family history of stroke.
How can stroke affect you?
Although stroke is a disease of the brain, it can affect the entire body. A common disability that results from stroke is complete paralysis on one side of the body, called hemiplegia. A related disability that is not as debilitating as paralysis is one-sided weakness or hemiparesis. Stroke may cause problems with thinking, awareness, attention, learning, judgment, and memory. Stroke survivors often have problems understanding or forming speech. A stroke can lead to emotional problems. Stroke patients may have difficulty controlling their emotions or may express inappropriate emotions. Many stroke patients experience depression. Stroke survivors may also have numbness or strange sensations. The pain is often worse in the hands and feet and is made worse by movement and temperature changes, especially cold temperatures.
What can be done to decrease the stroke risk?
To reduce your risk of stroke, monitor your blood pressure, track your cholesterol level, stop smoking, exercise regularly, and find out if you should be taking a drug to reduce blood clotting.









