Treatment procedure of hepatitis E?

Apr 19, 2022
Hepatitis E is a subset of the group of virus-related liver inflammation. Persons between the ages of 15 and 40 are particularly affected by this disease.
For hepatitis E, it should be noted that there are no known chronic forms of the disease. It is only an acute form known. The sick persons usually feel only mild discomfort. The symptoms are not only light but sound in most cases, after about six weeks time off. However, there are also isolated cases of the disease, which can lead to deadly disease. Especially pregnant women are at risk of dying from acute and often fatal liver failure.

Comparing Hepatitis E with the other types of virus-induced liver inflammation, show many parallels to the Hepatitis A. Hepatitis E was even diagnosed as hepatitis A until 1980 and only then classified as a separate disease.
Diagnosis & disease course of Hepatitis E :
History : The attending physician will typically first perform an anamnesis of the patient. In doing so, he asks the patient what kind of symptoms he has and, above all, whether he has recently been abroad. Because the symptoms of hepatitis E are often relatively mild, it is relatively difficult to detect.
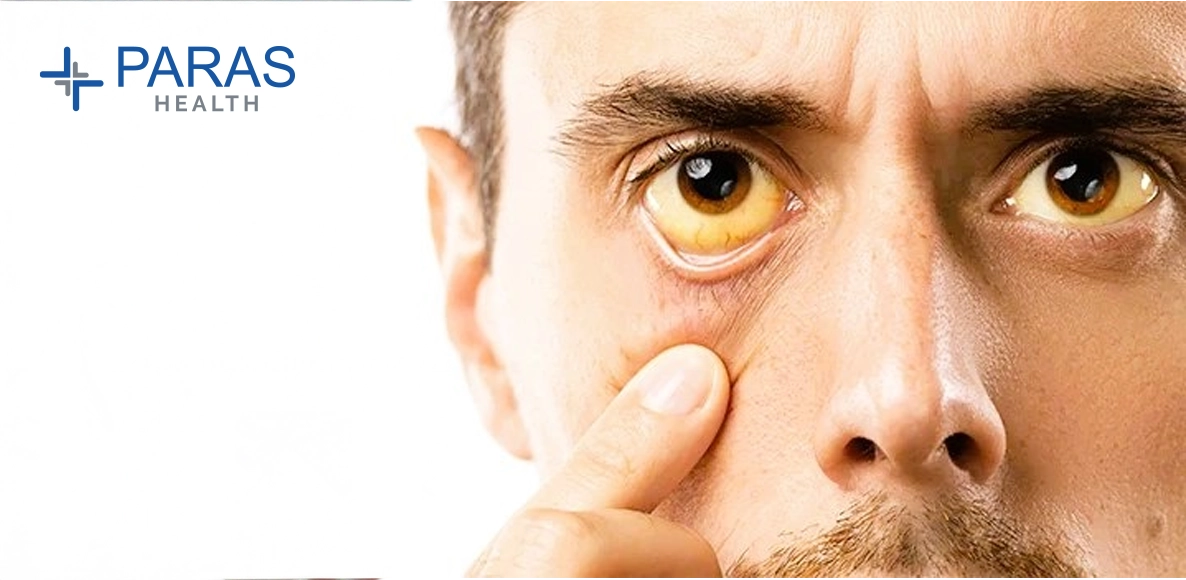
Checking for signs and symptoms : The internist will look for pain in the upper abdomen, flu symptoms or jaundice. Especially the decision between hepatitis E and hepatitis A is ambiguous. After all, the symptoms are almost congruent. But the Epstein Barr virus or flu could explain the complaints of the patient. For this reason, it is not enough to scan the patient for the most accurate diagnosis possible.
Hepatitis E has a long disease course:
Hepatitis E has a very long disease course due to its relatively extended incubation period of up to two months. Finally, it takes some time for the first symptoms to appear. As has already been said, the symptoms are similar to those of hepatitis A. However, the signs of hepatitis E can be a lot easier. However, the rate of mortality is about 0.4 – 5%. The likelihood of a fatal illness is about 20%. A chronic form of hepatitis E is only possible if organ transplantation has been performed.
The treatment of acute hepatitis E is purely symptomatic, so that prevention (hygiene) must make the most significant contribution to preventing the disease here. In immunocompetent persons, the course is usually unproblematic.

.png)
.jpg)